Building for neurodiversity: guidelines address final frontier of inclusive design
A first-of-its-kind published national guidance has been developed for building designers and planners to improve accessibility for neurodiverse people.
[edit] First-of-its-kind standard
BSI has launched a first-of-its-kind standard on the design of the built environment for a neurodiverse society.
Neurodivergence includes people with autism, ADHD, dementia, and a range of other sensory and/or information processing differences. It is estimated that around 1 in 7 people in the UK are neurodivergent in some form.
The guidance from BSI contained within the new standard, PAS 6463, applies to buildings and external spaces for public and commercial use, as well as residential accommodation for independent or supported living.
A significant number of people find elements of the built environment uncomfortable, distressing or a barrier to their use. For example, when interacting with the built environment, neurodivergent and neurodegenerative people can frequently experience 'sensory overload', overstimulation of the body's senses leading to a feeling of being overwhelmed. The increased demand on an individual of the associated cognitive load can lead to increased anxiety, fatigue and, in some cases, poor mental health.
[edit] PAS 6463, Design for the mind
PAS 6463, Design for the mind – Neurodiversity and the built environment – Guide aims to assist building designers in mitigating and eliminating these negative impacts.
Scott Steedman, Director-General, Standards at BSI, said: "Everyone deserves to experience the built environment in a way that supports their general wellbeing and generates better health outcomes. The new guidance within PAS 6463 fills a gap in design practice by addressing the needs of people whose minds process information and experiences differently, extending the benefit of inclusive design to a new and important community. With PAS 6463, designers can now benefit from guidance on lighting, decor, acoustics, and layout to support neurodiverse users of buildings and infrastructure."
Jean Hewitt, a senior member of the inclusive design team at Buro Happold and technical author of the PAS, added: "In addition to designing places to accommodate our diversity in form, size and physical ability, there is also a profound need to design for neurological difference. Since my first involvement in this area in 2009, I have hoped for some progress for the many neurodivergent colleagues, friends, and family whose lives are unnecessarily blighted by places that don't work for them. Some have a formal diagnosis, but many do not; there are also many neurotypical people more mildly but regularly affected by environments on a day-to-day basis, perhaps triggering unsteadiness, migraines or experiencing extra daily stress through elements that are not intuitive or comfortable for them.
"My learning throughout the process of developing this PAS leads me to believe at least 30% of the population are negatively impacted by elements that could so easily be adjusted or eliminated during design, procurement, and management without any cost implications. This PAS is an opportunity to ask everyone involved in the built environment to carefully consider this normal neurological diversity of humans rather than just meeting basic regulatory demands – places should be comfortable for everyone to visit and use without encountering emotional distress or difficulty. I'm very excited to have been involved in developing this guidance to help make this the case for many more people."
This article first appears on the CIAT news and blog site as "Building for neurodiversity: guidelines address 'final frontier of inclusive design'" dated October 17, 2022.
--CIAT
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Adapting homes for dementia.
- Autism and the workplace.
- Autistic masking.
- Dementia-friendly home.
- Dementia and the built environment.
- Diversity in the construction industry.
- Diversity and the housing crisis.
- Diversity in regeneration.
- Neurodiversity in the built environment.
- Nature and Wellbeing: The Evidence.
- People with disabilities definition.
- Special educational needs: an analysis of the necessities for inclusion.
- Wood and educational buildings.
Featured articles and news
Private rental sector, living standards and fuel poverty
Report from the NRH in partnership with Impact on Urban Health.
.Cold chain condensing units market update
Tracking the evolution of commercial refrigeration unit markets.
Attending a conservation training course, personal account
The benefits of further learning for professsionals.
Restoring Alexander Pope's grotto
The only surviving part of his villa in Twickenham.
International Women's Day 8 March, 2025
Accelerating Action for For ALL Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.
Lack of construction careers advice threatens housing targets
CIOB warning on Government plans to accelerate housebuilding and development.
Shelter from the storm in Ukraine
Ukraine’s architects paving the path to recovery.
BSRIA market intelligence division key appointment
Lisa Wiltshire to lead rapidly growing Market Intelligence division.
A blueprint for construction’s sustainability efforts
Practical steps to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Timber in Construction Roadmap
Ambitious plans from the Government to increase the use of timber in construction.
ECA digital series unveils road to net-zero.
Retrofit and Decarbonisation framework N9 launched
Aligned with LHCPG social value strategy and the Gold Standard.
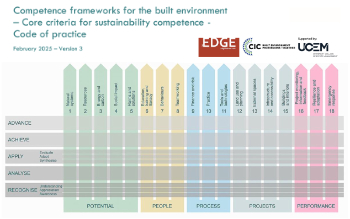
Competence framework for sustainability
In the built environment launched by CIC and the Edge.
Institute of Roofing members welcomed into CIOB
IoR members transition to CIOB membership based on individual expertise and qualifications.
Join the Building Safety Linkedin group to stay up-to-date and join the debate.
Government responds to the final Grenfell Inquiry report
A with a brief summary with reactions to their response.